Varicose veins are a pathology of venous vessels, in which the functioning of the vein valves is disrupted and blood penetrates downwards.Stagnation appears, blood flow is disrupted, and the venous wall loses its elasticity.Enlarged veins become visible to the naked eye.Externally through the skin, they resemble dense thick worms with a bluish tint.At the initial stage, “spider veins” are formed.
Varicose veins during pregnancy.What is it

During pregnancy, weight progresses due to the growth of the fetus.Accordingly, increased body weight “puts pressure” on the legs, leading to expansion of the venous walls.
A cosmetic defect of the lower extremities can develop into a huge problem with dire consequences.
The expansion of venous walls during the gestational period requires treatment and compliance with preventive measures to combat the disease.
Stages of varicose veins formation:
- At the beginning of the development of the disease, there are no clinical signs of the disease.Swelling of the limbs may occur.Upon external examination, a web of small vessels appears.
- At the next stage, deformation of the venous wall occurs: loss of elasticity, thickening and slowing of blood circulation.Pain syndrome and increased fatigue of the calf muscles appear.
The process is aggravated by the influence of the uterus, which increases in size.
Dilated veins during pregnancy are observed on the lower extremities, labia, and anus.
Causes of varicose veins in pregnant women
The main cause of the pathology is weight gain.
However, most pregnant women gain weight.But this does not mean that everyone is diagnosed with venous disease.
For the development of the process, more compelling reasons and factors are needed.
These include:
- Varicose veins in close relatives (hereditary factor);
- Hormonal changes and imbalances;
- Congenital anomalies of the venous system;
- Injuries of veins and arteries;
- Chronic liver diseases;
- Changes in the consistency and thickness of biological fluid;
- Disturbance of the hemostasis system.
Venous expansion occurs not only in the legs, but also in the groin and pelvis.
Factors that provoke disease on the legs
- Intestinal diseases with a tendency to form difficult bowel movements (constipation);
- Exceeding the permissible body weight (even in an “interesting position”);
- Sedentary lifestyle;
- Work that requires constant sitting at a desk.
Small pelvis

- Carrying several fetuses at the same time or a large weight of the unborn child;
- Endometritis;
- Multiple pregnancies;
- Thrombophlebitis;
- Inflammation of the appendages;
- Thrombosis of uterine vessels;
- Neoplasms in the reproductive organs.
In the groin
- Gynecological pathologies in complex;
- Prolonged hormone therapy;
- A significant number of pregnancies in history;
- Several short-term pregnancy terminations;
- Increased estrogen;
- “Sedentary” professional activity.
Types and symptoms of varicose veins during pregnancy
The type of inflammation is related to the place of its manifestation.
There are dilation of blood vessels in the systemic circulation:
- On the legs - occurs in 80% of cases and is mainly associated with changes in severity during gestation;
- In the small pelvis – 8–10%.It often occurs in non-pregnant patients, and with the onset of an “interesting situation” it worsens.
- Inguinal zone - vascular dilatation is common, spider veins appear.
Symptoms of pathology
The clinical picture of varicose veins differs in its location and the severity of inflammation.
General signs of pathology development:
- General fatigue;
- Heaviness in the legs;
- The appearance of small vascular branches visible through the skin;
- Slight burning along the vessel.
Symptoms according to the location of the disease:
Lower limbs:
- Swelling;
- Increased sweating and unpleasant odor;
- Cramps during night sleep;
- Frequent feeling of “running goosebumps”;
- Tired legs;
- Soreness in the feet;
- Stiffness in movement of the affected limb.
In the pelvis:
- Pain in the perineal area;
- Nagging pain in the lower abdominal segment;
- Changes in the nature of vaginal secretions;
- Dilated veins on the labia or at the entrance to the vagina;
- Pain during sexual intercourse;
- Uterine tone.
In the groin:
- Feeling of fullness and burning in the groin area;
- Minor hyperthermia;
- Vascular web;
- Protrusion of veins;
- Itching.
What are the dangers of varicose veins during pregnancy?
Venous pathologies detected during the gestational period can lead to complications during gestation and during labor.
The danger of congestive blood phenomena is the increased risk of blood clots and the development of thromboembolism at the time of childbirth.
The pathology causes venous insufficiency, which cannot but affect the well-being of the pregnant woman and the health of the fetus.
Varicose veins are a precursor to thrombosis, which can “block” the access of oxygen in the uterine bloodstream.This pathology leads to intrauterine death of the unborn child.
A mild form of pathology does not have a negative effect on the fetus, but requires mandatory monitoring by doctors.
Dilatation of veins with constant pressure leads to the development of thrombophlebitis, trophic ulcers and thrombosis of deep vessels.
Diagnosis of varicose veins in pregnant women
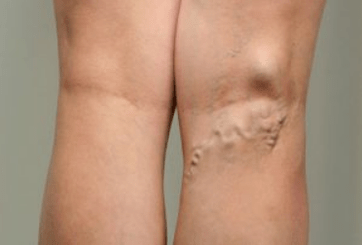
Pathology can be suspected in two cases:
- Visually notice an increase or protrusion of blood vessels;
- Assess existing symptoms.
In both cases, specialized diagnostics are required.
During a routine examination, the gynecologist takes into account the patient’s complaints and, if necessary, sends her for additional examination.
It is important to pay attention to the fact that from the 20th week of gestation until the time of birth, fatigue in the legs is inherent in every second pregnant woman.But this is by no means a symptom of the spread of vascular pathology.
Diagnostic manipulations will confirm or refute the suspicions of the pregnant patient.
The main diagnostic methods are carried out only by an “expert” of veins - a phlebologist.To identify the cause, hardware methods are used:
- Duplex scanning of veins;
- Vascular ultrasound;
- In severe cases - contrast venography.
In addition, the specialist will collect anamnesis, take into account complaints and recommend taking the necessary tests.
Treatment of disease during pregnancy
The therapy used is intended to eliminate the main symptoms of the pathology and restore normal blood circulation.
The treatment tactics carried out must be well thought out in order to minimize the possible negative impact on the pregnant child.
Compression therapy
Wearing therapeutic stockings with a compression function is the main treatment for varicose veins in pregnant patients.
Stockings and tights perfectly maintain pressure in the blood vessels, preventing them from bulging.The special fabric of the underwear allows air to pass through, so your feet do not sweat.
Therapeutic knitwear restores the circulatory system and prevents the development of thrombosis.
Compression products relieve inflammation and fatigue in the legs.
Drug treatment
To eliminate the pathology, topical medications are used.These are creams, ointments and special rubs.Preparations based on chestnut are popular.
Oral therapy consists of taking heparin-based anticoagulants to maintain the hemostatic system.
Heparin drugs reduce the risk of blood clots by thinning the blood to the desired consistency.
Recommendations for the prevention of varicose veins in pregnant women
To minimize the occurrence of pathology during the gestational period, it is necessary to follow preventive measures:
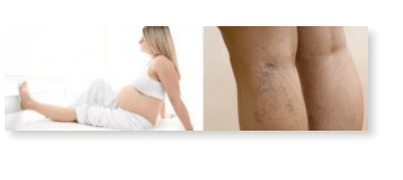
- Follow the diet of pregnant women, controlling body weight;
- Give preference to comfortable shoes;
- Reduce consumption of harmful foods;
- Take a walk every day with a fifteen-minute break;
- Follow a diet to eliminate constipation;
- Do not wear jeans or too tight trousers;
- To prevent protrusion of vascular walls with a hereditary predisposition to wear compression garments;
- Lead a healthy lifestyle without smoking tobacco or drinking strong alcoholic beverages.