Varicose veins are changes in the veins of the legs, their shape, structure and functionality.
Varicose veins (VVs) most often occur in the legs. This is the "payment" for upright posture, namely, the load on the veins of the lower extremities is very high, so they often suffer from dilatation or expansion.
In the ICD, the disease is encrypted with code 183, it is widespread throughout the world and is found everywhere in all countries.
general information
The pathology is the most common, the incidence is 60% among the adult population. Varicose veins in the legs in the initial stages are not noticed in most cases, since there are no clinical manifestations yet.
Causes
A single specific cause of leg vein disease is unknown, but doctors identify risk factors or situations that create favorable conditions for varicose veins:
| Causes of varicose veins | Peculiarities |
|---|---|
Genetic predisposition |
The disease is often "passed on" by inheritance from close relatives. Most often, the basis is a mutation of genes that are responsible for the consistency of the vascular wall. Mutated genes cannot work normally and the tone of the venous wall decreases, it becomes "weak" and stretches, which in turn leads to the development of valvular insufficiency and the appearance of reverse blood flow in the veins. In the absence of treatment and prevention, varicose veins "descend" lower, and nodes and lumps gradually form. |
Age |
The older the person, the higher the likelihood of the disease. |
Female |
Men get sick much less often. |
Obesity |
A sedentary lifestyle and the accumulation of visceral fat affect the walls of blood vessels. |
With hormonal imbalance, a decrease in the tone of the venous network occurs. Experts are confident that the etiological factor in most cases is a violation of the venous outflow in the lower extremities.
How the disease develops
The most important thing in the development of this pathology is a change in the condition and functional activity of the veins. As a result of "breakage, " the walls of blood vessels and valves are damaged – reflux develops, which in turn "stretches" the veins even more and worsens their condition.
As the pathology develops, connective tissue grows in the muscle layer of the vein, after which it atrophies and the collagen framework of the vessel is destroyed. The vessels lose their elasticity, while the functioning of the valves is also disrupted and blood circulation worsens even more. The veins swell and swell, taking on a swollen appearance.
Signs of varicose veins
The first symptoms can be missed - few of us pay attention to the pastiness and heaviness of the legs, especially in the evening after work. The veins are not yet visible visually, so at this stage people rarely seek help from a doctor. Although it is not necessary to treat at this stage, you can only change your lifestyle and thus slow down the development of the pathological process. Varicose veins in the legs can manifest themselves as:
- Color change.Occurs as the disease progresses. The skin over the veins can change its properties, including color. Blue veins with a convoluted shape may also attract attention, causing aesthetic discomfort.
- Rashes.In some patients, the legs may become covered with itchy blisters, nodules and redness. These symptoms may disappear on their own after a long night's rest in a horizontal position.
- Chronic form.If the signs do not disappear even after a night's sleep, this may indicate chronic venous insufficiency and a severe stage of the disease. Patients may also complain of pain in the calf muscles and increased leg fatigue.
Trophic disorders are a consequence of the progression of the disease in the absence of treatment, which often takes years and decades. They begin with skin manifestations:
- hyperpigmentation - the appearance of brown spots,
- venous eczema and lipodermatosclerosis, that is, skin thickening.
It is important to note the fact that venous disease of the lower extremities can worsen with a decrease in physical activity, for example, if a person stands or sits for a long time during the working day. But during active movements, for example, when walking, the discomfort decreases. Another relief comes from wearing compression stockings and resting in a horizontal position.
Burning or tingling, cramps of the calf muscles or restless legs syndrome (unpleasant sensations in the legs at rest, when the body literally requires them to move in order to eliminate this discomfort) - in most cases, they are still neurological symptoms and accompany pathologies such as, for example, radicular syndrome.
Note!The intensity of complaints and unpleasant symptoms may be periodic: venous symptoms are more pronounced in the warm season or during menstruation in women.
Complications of changed veins in the legs
As the disease progresses, microcirculation and metabolic processes are so disrupted that trophic ulcers may form or even thrombosis of damaged veins and bleeding from varicose "nodes" may develop.
Disease of the veins in the legs is fraught with thrombophlebitis, which can cause pulmonary embolism. Bleeding from affected veins leads to large blood losses and anemia.
Which doctors should I contact?
If veins protrude on the legs and feet, this is a reason to contact a specialist. Most often, patients turn to a surgeon. If concomitant diseases are identified, it is necessary to visit a cardiologist, phlebologist, endocrinologist, or therapist.
Diagnosis of the disease
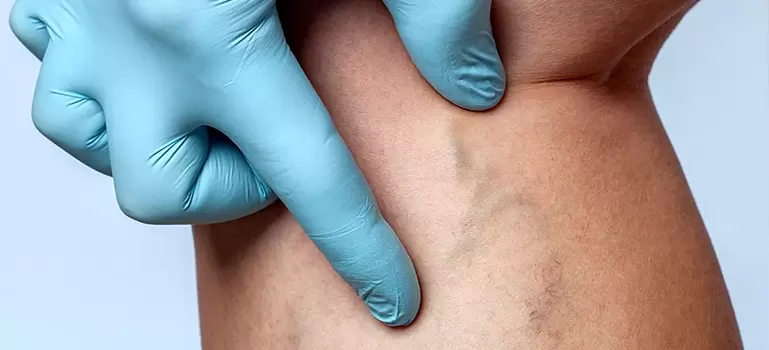
As a rule, making a diagnosis does not cause difficulties. Initially, the doctor relies on the patient’s complaints and examination data. When collecting an anamnesis, attention is drawn to swelling and heaviness in the legs; upon examination, the doctor sees dark, tortuous veins, and in severe cases, lumps and bumps.
To confirm the diagnosis, instrumental research methods are prescribed, the main and leading of which is ultrasound duplex scanning or abbreviated USDS. Thanks to it, you can quickly, accurately and effectively determine the source of varicose veins, assess the structure and condition of the vessel, the functional characteristics of the venous valves, the presence/absence of blood clots and the amount of reverse blood flow.
During ultrasound scanning, the specialist examines both the deep and superficial venous systems.
To assess valve function and the extent of reflux, the following may be done:
- compression tests - pressing on different parts of the legs of the lower extremities;
- straining test;
- reaction to taking Paran.
Based on the results of the study, the specialist draws a special "venous map", which he needs to think about treatment tactics.
If additional research methods are necessary, the doctor may also prescribe: Doppler ultrasound, phlebography with contrast, CT or MRI, thermography, intravascular ultrasound (IVUS).
What to do
If the veins in your leg are swollen, you must adhere to a certain diet prescribed by your doctor. Physical activity should be moderate, shock loads should be avoided, massage, baths, saunas are contraindicated. To improve blood flow and train the venous walls, contrast baths are recommended.
Treatment of varicose veins
The main goal of therapy is to eliminate all veins that are not working correctly. In fact, this is possible with the help of invasive intervention: removal, sclerosis and obliteration. This helps to remove the root cause, and not just the unpleasant symptoms. Treatment methods for varicose veins are selected by doctors based on the clinical picture.
Removal
Removal is the oldest, and for a long time, the only effective way to get rid of varicose veins. First, the doctor ties the anastomosis, that is, the junction of the common femoral and great saphenous veins, and after that the affected vein is removed.
This helps cure the disease, but this method has its drawbacks - the need for anesthesia, long recovery, the presence of incisions and stitches.
Endovenous laser or radiofrequency obliteration
During the procedure, the affected veins are "brewed", after which they stop working and gradually dissolve. This procedure allows you to quickly and safely eliminate varicose veins without incisions or scars. Obliteration is called "office surgery", it is assumed that a person can undergo treatment during his lunch break - quickly and safely, and then return back to work.
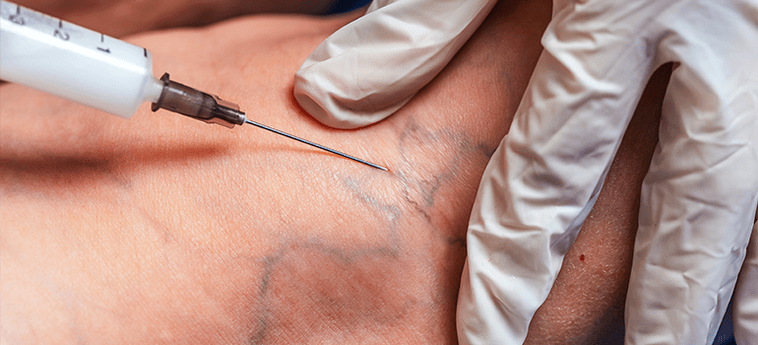
Sclerotherapy
"Gluing" or mechanochemical obliteration is a procedure during which the doctor uses a thin needle to inject a special solution, a sclerosant, into the damaged vein. This substance glues the walls of the vessel and turns it off from the bloodstream, and over time such a vein completely disappears.
The drug is safe for health and remains in the place where it was administered without spreading throughout the body.
Note!After the procedure, elastic compression is applied and the patient is advised to spend an hour actively - walking and warming up. The bandages are not removed for 10-14 days, after which the use of compression garments is recommended.
FAQ
How do veins hurt in the legs and what are the symptoms?
Clinically, varicose veins of the feet and legs are manifested by pain in the calf muscles, a feeling of heaviness, cramps, skin itching, and pasty limbs in the evening.
Why do varicose veins appear and what do they look like?
At the initial stages, varicose veins are not noticeable. Then dark veins are visualized, curved, sometimes "branchy". At a severe stage, you can see nodes and bumps, and if complications develop, you can also see trophic ulcers on the legs.
Why is vein disease in the legs more common?
This is due to the fact that during long periods of sitting or standing work, blood stagnation occurs in the vessels of the legs. If this situation lasts for one day or even a week, nothing bad will happen.
Expert opinion
Very often, different people suffer from veins in their legs. This is due to the fact that man is an upright walking creature. We spend a lot of time on our feet or sitting in the office. This leads to poor circulation in the lower extremities and fluid stagnation. This in turn affects the veins, worsening their condition and functional activity.
To cure varicose veins, you need to contact a competent specialist - he will conduct an examination and select the most effective therapy to eliminate not only the symptoms, but also the root cause of the pathology.